
10 Types of Programming Languages Every Coder should Know
Learn about different types of programming languages and how they are implemented in the real world.

The goto statement in C language is used to jump from one part of the source code to another. It can be very helpful in certain situations where other control statements might need to be more effective. Goto statements can be used in two ways: skip some lines and move to a block below in the source code or repeat some lines of source code by going above in the source code. This article also explained the ‘goto’ statement in C language. Its disadvantages of goto
The ‘goto’ statement in C is a control flow statement that allows you to jump to another point in the program. It is generally recommended to use structured control flow statements like loops and conditionals, ‘goto’ can be useful in certain situations, particularly when handling errors or breaking out of deeply nested loops.

POSTGRADUATE PROGRAM IN
Multi Cloud Architecture & DevOps
Master cloud architecture, DevOps practices, and automation to build scalable, resilient systems.
The syntax of the goto statement can be defined in two parts:
Style 1: Down to the top declaration of the goto statement in C
label_name:
.
.
.
goto label_name;
Style 2: Transferring the control from top to down
label_name:
.
.
.
goto label_name;
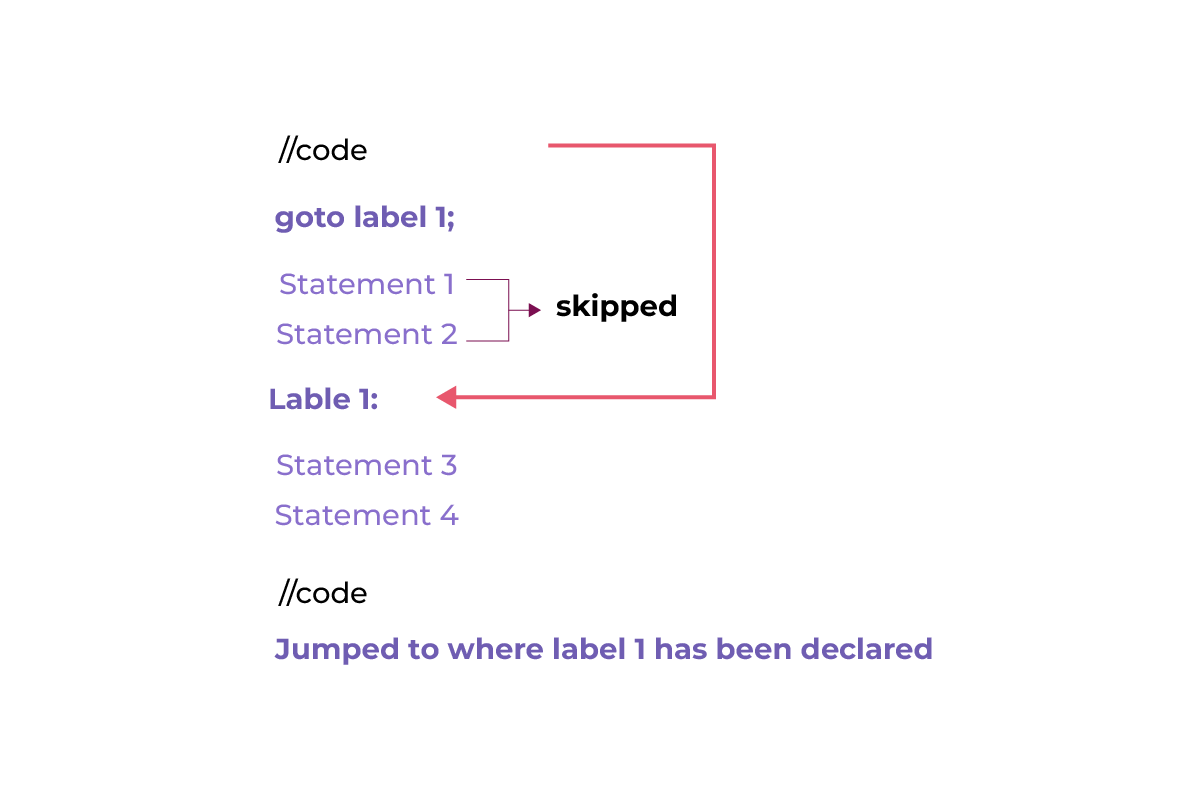
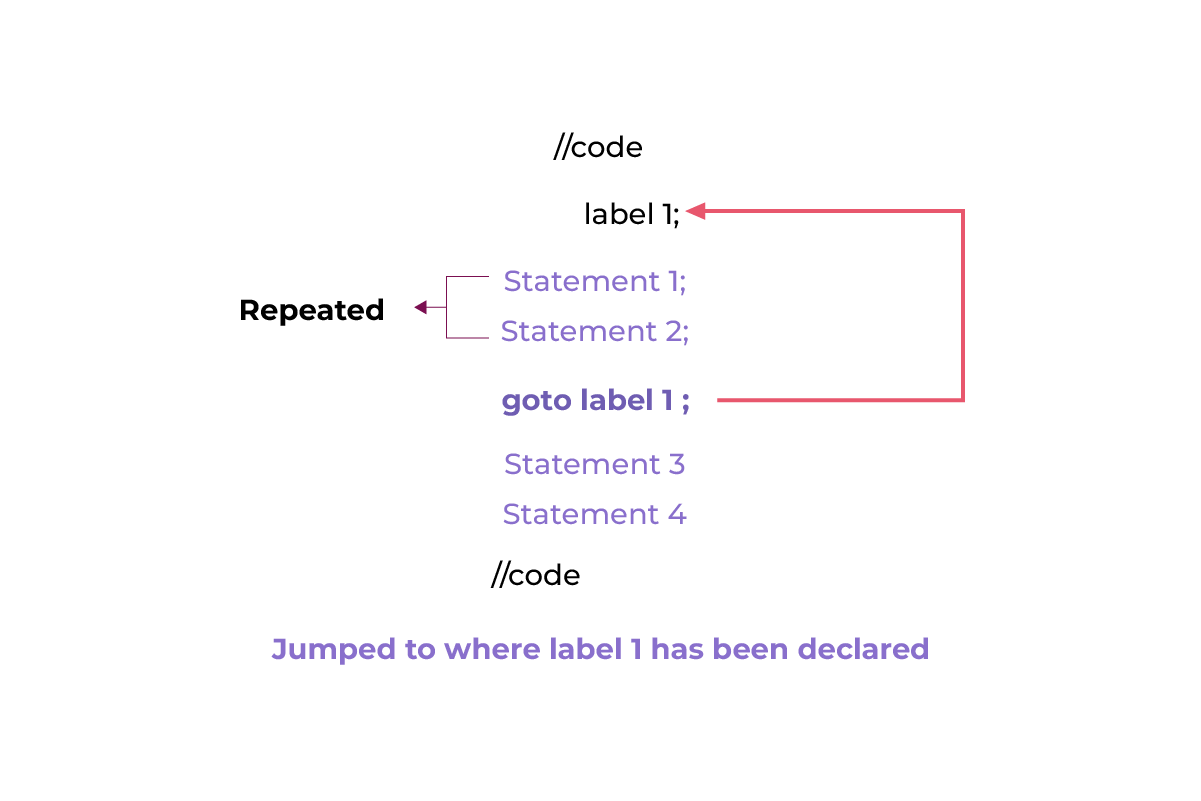
As shown in the flow diagram, when the program encounters a goto statement, the control immediately jumps to the location where the corresponding label is defined.
In the scenario where the label is defined after the goto statement, the program skips over any statements between the goto statement and the label.
Conversely, no statements are skipped if the label is declared before the goto statement. Instead, the statements between the goto statement and the label are executed again, effectively repeating them.
Let’s look at examples of ‘goto’ statements in the C language:
Example 1: Basic Use of ‘goto’
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
int x = 10;
if (x == 10) {
goto label1; // Jump to label1
}
printf("This line will be skipped if x is 10.\n");
Label1:
printf("This line is executed because x is 10.\n");
return 0;
}
Output
This line is executed because x is 10.
The above program checks whether the condition is equal to 10. If it is, the goto label1 statement transfers control to the label1 function and directly executes the code after the label.
Example 2: The following program demonstrates the ‘goto’ for Error Handling
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
int a = 10, b = 0;
int result;
if (b == 0) {
goto error; // If b is zero, jump to the error handling code
}
result = a / b;
printf("Result: %d\n", result);
return 0;
error:
printf("Error: Division by zero!\n");
return -1;
}
Output
ERROR!
Error: Division by zero!
82.9%
of professionals don't believe their degree can help them get ahead at work.
The ‘goto’ statement in C is often criticised, but it does have some advantages in certain scenarios. Let’s see some potential benefits of using ‘goto’:
The ‘goto’ statement in C language allows an unconditional jump to a labelled statement within the same function. Imagine having more than two or three goto statements in a program and figuring out which one is leading the program. It can become difficult to understand the new flow when goto statements are added. This makes the source unreadable and dirty.
The following program demonstrates the show goto Statement in C language:
Program
#include <stdio.h>
int main(){
int n = 5;
int ans = n;
start :
ans += n;
if(ans%2==1){
goto odd;
}
if(ans%2==0){
goto start;
}
odd :
printf("%d", ans);
return 0;
}
Output
15
The ‘goto’ statement in C allows an unconditional jump to a labelled statement. It can simplify certain tasks but often results in less readable and maintainable source code. Modern programming practices generally prefer structured control flow mechanisms like loops and conditionals over ‘goto’ to avoid potential pitfalls such as increased complexity and difficulty in debugging. It is used ‘goto’ sparingly and only when it improves source code clarity or simplifies complex logic.
Updated on August 31, 2024

Learn about different types of programming languages and how they are implemented in the real world.

Explore 10 front-end development, including key languages, its advantages and disadvantages, and how it shapes user experience in web design and functionality.